

WEB RTMP PRO
More detail can be found in the Red5 Pro Documentation. Under the operating logic of a Stream Manager– a Red5 Pro Server Application that manages traffic and monitors server usage– clusters or NodeGroups– a group of one or more active server nodes– are established in the geographic regions where the streaming will be happening. Red5 Pro reimagined the entire architecture from back-end server to front-end browser and mobile app integration.īy leveraging cloud infrastructure, Red5 Pro’s Autoscaling Solution automatically scales the system up or down in response to current conditions. However, some creative reconfiguration of scaling infrastructure resulted in the cloud-based Red5 Pro Autoscaling Solution supporting millions of concurrent connections all with under 500 milliseconds of latency. Under traditional modes of thinking this was technically true. There is a common misconception that WebRTC is not scalable due to how it establishes a peer-to-peer connection.
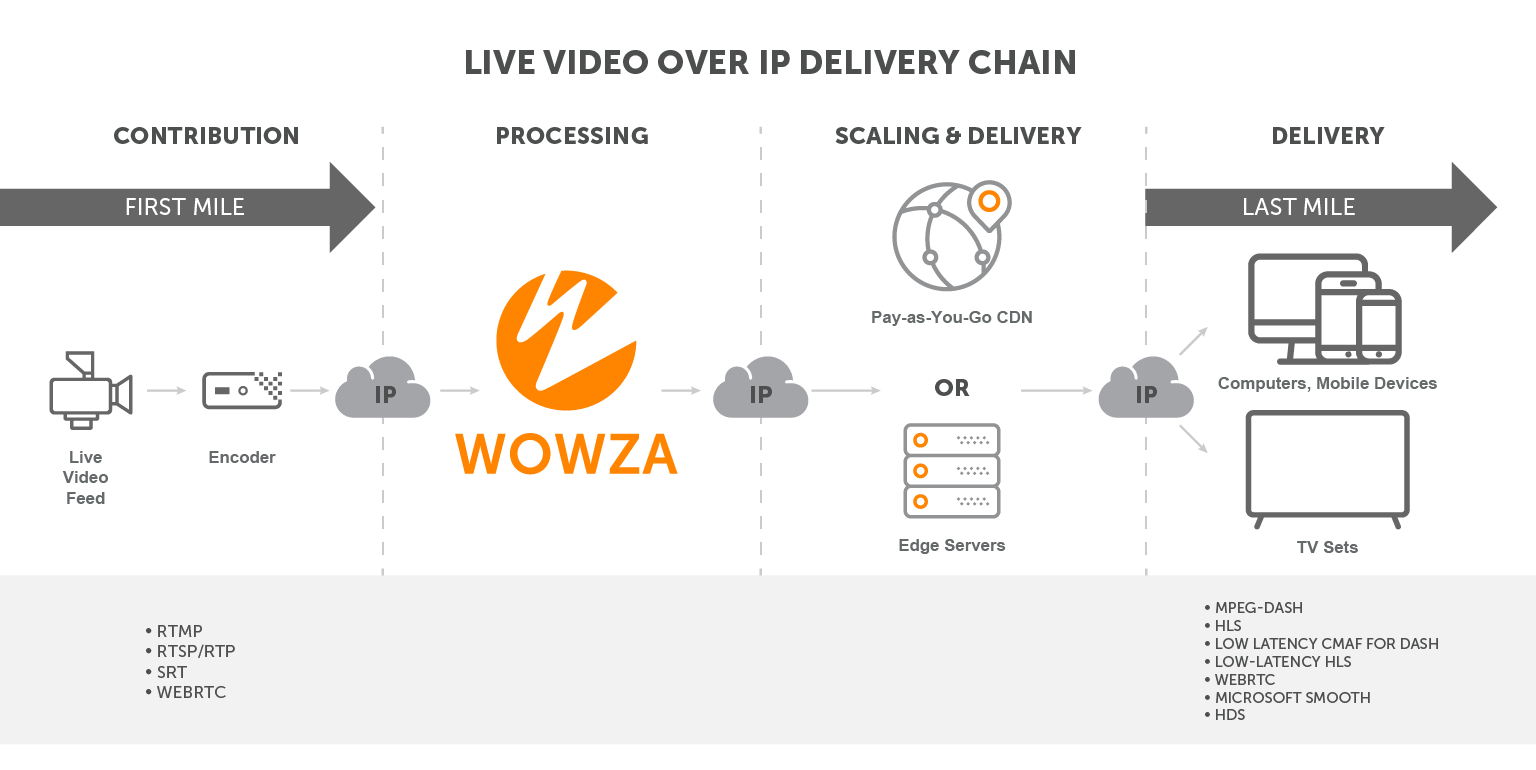
For the best performance and distribution of streams, multiple server instances are necessary. No matter what protocol is used, it will need to handle multiple broadcasters and subscribers.
WEB RTMP CODE
All the decoding (and encoding for that matter) is performed directly in native code so it can be rendered directly in the browser.Īgain, HTTP based streaming protocols such as HLS or MPEG DASH are capable of video egress, but they are not a practical choice for low latency streaming.įor more detail on how RTMP works, take a look at our other blog post. Since WebRTC works natively in the browsers, you can connect to an egress WebRTC server and consume a video stream over SRTP. Not only can WebRTC can perform the work of broadcasting (ingest) but it works for receiving video (egress) as well. Technically HTTP based protocols such as HLS or CMAF could be considered a replacement but their lackluster performance does not make them a viable option for real-time live streaming video. In short, there are two replacements for RTMP SRT for hardware encoders, and WebRTC for browsers. It can also still maintain a high-quality video, even in less than ideal network conditions. By using an efficient UDP based transport known as SRTP, WebRTC is able to transport video with the lowest latency currently possible. Its tech stack allows for camera and microphone access on various devices.

On the other hand, WebRTC does work in browsers. As SRT was originally designed for hardware encoders and has yet to be adopted as a Web standard, it’s not available in modern browsers. SRT is an open-source video transport protocol and technology stack that optimizes live stream delivery through firewalls and across unreliable networks. We can approach it from both sides of creating a live stream: ingest (broadcast) and egress (subscribe).īoth SRT (Secure Reliable Transport) and WebRTC are good options for ingesting live streams with minimal latency. Now that we’ve established the need, how do we actually achieve sub-second latency. As more and more users expect high speeds, the products they use will reflect that expectation. Additionally, ever-increasing smartphone adoption is further fueling the demand for real-time latency. The only way to have truly interactive experiences with natural conversation is with the lowest possible latency. As we’ve discussed before live streaming should be live and that means delivering media at the fastest possible speed. This makes latency a critical consideration.įurthermore, low latency is necessary for creating high-value streaming applications. However, as RTMP created a delivery method for low latency video streaming, so too will the new protocols need to focus on latency as well. Quite simply, RTMP will be replaced by modern protocols. That leads to the question of “What’s next for RTMP servers?” By losing Flash, we also lose the ability to run RTMP in internet browsers. The new year of 2020 marks the last year of official Flash support. However, there are big changes coming for Flash. RTMP was designed for delivering on-demand media and live media (i.e live audio, video, and data) over the Internet between a Flash player and a Media Server. Originally developed by Macromedia and now owned by Adobe. RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) has a long-established history as one of the original methods for live streaming.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
